[作者-陈君|编辑-王欣芮|审核-刘心月]近日,人工智能领域顶级国际会议ICML 2025(Forty-Second International Conference on Machine Learning,CCF-A类)公布论文接收结果,录用了信息学院陈洪教授课题组在机器学习理论领域的研究成果。
Jun Chen, Hong Chen, Yonghua Yu, Yiming Ying, How does Labeling Error Impact Contrastive Learning? A Perspective from Data Dimensionality Reduction, ICML 2025
该研究论文题为“How does Labeling Error Impact Contrastive Learning? A Perspective from Data Dimensionality Reduction”,系统性地分析了传统数据降维对自监督对比表示学习的理论影响.近年来,对比学习在自监督表示学习领域取得了先进的性能。许多先前的研究试图从理论层面解释对比学习成功的原因,但这些理论分析几乎都依赖于标签一致性假设,即通过数据增强生成的正样本对语义一致。然而,在实际应用中,由于常见数据增强策略的强度和随机性,可能产生标签误差,导致该假设不成立。本文从理论角度研究了标签误差对对比学习下游分类性能的影响。具体来说,本文首先揭示了标签误差对下游分类风险的多种显著的负面影响。为缓解这些影响,研究提出在原始数据上应用传统数据降维方法(如奇异值分解SVD)以减少假阳性样本,并通过理论和实验验证其有效性。进一步的研究发现,SVD是一把双刃剑:其虽然能降低标签误差,但可能因削弱增强图的连通性而导致下游分类精度下降。基于上述发现,本文提出以下数据增强的建议:应采用中等嵌入维度(实验中取512或1024)、数据膨胀、弱增强以及SVD相结合的策略,在保证增强图高连通性的同时减小标签错误,从而提升模型性能。
信息学院2022级博士研究生陈君为论文第一作者,陈洪教授为通讯作者,悉尼大学应益明教授、工学院博士研究生余勇华参与了论文的研究工作。该研究获得了国家自然科学基金面上项目等的资助。
会议链接:https://icml.cc
【英文摘要】In recent years, contrastive learning has achieved state-of-the-art performance in the territory of self-supervised representation learning. Many previous works have attempted to provide the theoretical understanding underlying the success of contrastive learning. Almost all of them rely on a default assumption, i.e., the label consistency assumption, which may not hold in practice (the probability of failure is called labeling error) due to the strength and randomness of common augmentation strategies, such as random resized crop (RRC). This paper investigates the theoretical impact of labeling error on the downstream classification performance of contrastive learning. We first reveal several significant negative impacts of labeling error on downstream classification risk. To mitigate these impacts, data dimensionality reduction method (e.g., singular value decomposition, SVD) is applied on original data to reduce false positive samples, and establish both theoretical and empirical evaluations. Moreover, it is also found that SVD acts as a double-edged sword, which may lead to the deterioration of downstream classification accuracy due to the reduced connectivity of the augmentation graph. Based on the above observations, we give the augmentation suggestion that we should use some moderate embedding dimension (such as 512, 1024 in our experiments), data inflation, weak augmentation, and SVD to ensure large graph connectivity and small labeling error to improve model performance.
Zhihao Li, Xue Jiang, Liyuan Liu, Xuelin Zhang, Hong Chen, Feng Zheng, On the Generalization Ability of Next-Token-Prediction Pretraining, ICML 2025.
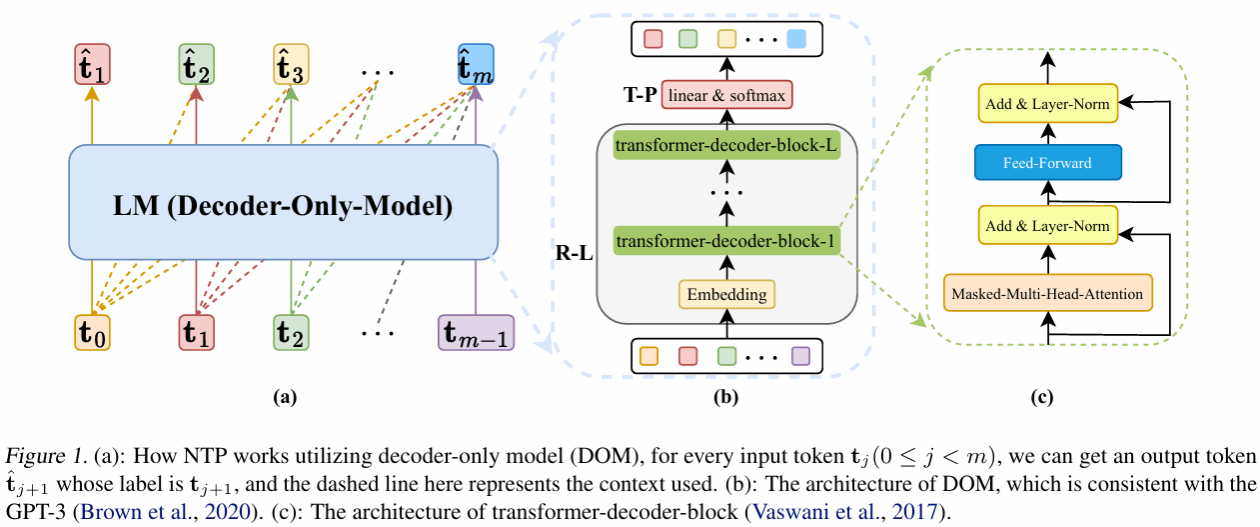
LLM在各种NLP任务中表现出色,尤其是在文本生成方面,这很大程度上取决于LLM在大规模无标签语料数据集上的预训练。当前主流的LLM如GPT、LLaMA、DeepSeek等均属于Decoder-Only模型 (DOMs),而DOMs的预训练任务均是:利用此前的所有token去预测下一个token,也就是Next-Token-Prediction (NTP)。尽管LLM的NTP预训练在工程技术方面已经取得了诸多进展,然而关于NTP预训练的理论分析,尤其是泛化理论分析仍然十分稀缺,几乎属于空白。为了填补这一空白,本文从传统的统计学习理论出发,对多层-多头DOMs的覆盖数进行了精细的分析,并基于Rademacher复杂度与混合过程给出了DOMs在NTP预训练任务中的超额风险上界。我们的理论结果表明,LLM的预训练泛化能力主要取决于模型参数量、token序列数量以及token序列长度这3个参数,当增大模型参数量时,应该以线性的比例同步增加预训练的总token数量,这与基于工程的Scaling-Laws的结论几乎一致。
【英文摘要】Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in handling natural language processing (NLP) tasks and beyond. LLMs usually can be categorized as transformer decoder-only models (DOMs), utilizing Next-Token-Prediction (NTP) as their pre-training methodology. Despite their tremendous empirical successes, the theoretical understanding of how NTP pre-training affects the model's generalization behavior is lacking. To fill this gap, we establish the fine-grained generalization analysis for NTP pre-training based on Rademacher complexity, where the dependence between tokens is also addressed. Technically, a novel decomposition of Rademacher complexity is developed to study DOMs from the representation learner and the token predictor, respectively. Furthermore, the upper bounds of covering number are established for multi-layer and multi-head transformer-decoder models under the Frobenius norm, which theoretically pioneers the incorporation of mask matrix within the self-attention mechanism. Our results reveal that the generalization ability of NTP pre-training is affected quantitively by the number of token sequences N, the maximum length of sequence m, and the count of parameters in the transformer model Theta. Additionally, experiments on public datasets verify our theoretical findings.
Chang Cao, Han Li, Yulong Wang, Rui Wu, Hong Chen, Adversarial Robust Generalization of Graph Neural Networks, ICML 2025.
【英文摘要】 We establish an adversarial generalization bound of general GNNs via covering number analysis.Abstract:While Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown outstanding performance in node classification tasks, they are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, which are imperceptible changes to input samples. Adversarial training, as a widely used tool to enhance the adversarial robustness of GNNs, has presented remarkable effectiveness in node classification tasks. However, the generalization properties for explaining their behaviors remain not well understood from the theoretical viewpoint. To fill this gap, we develop a high probability generalization bound of general GNNs in adversarial learning through covering number analysis. We estimate the covering number of the GNN model class based on the entire perturbed feature matrix by constructing a cover for the perturbation set. Our results are generally applicable to a series of GNNs. We demonstrate their applicability by investigating the generalization performance of several popular GNN models under adversarial attacks, which reveal the architectural factors influencing the generalization gap. Our experimental results on benchmark datasets provide evidence that supports the established theoretical findings.
Chang Cao, Han Li, Yulong Wang, Rui Wu, Hong Chen. Adversarial Training for Graph Convolutional Networks: Stability and Generalization Analysis, IJCAI 2025.
【英文摘要】Recently, numerous methods have been proposed to enhance the robustness of the Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) for their vulnerability against adversarial attacks. Despite their empirical success, a significant gap remains in understanding GCNs' adversarial robustness from the theoretical perspective. This paper addresses this gap by analyzing generalization against both node and structure attacks for multi-layer GCNs through the framework of uniform stability. Under the smoothness assumption of the loss function, we establish the first adversarial generalization bound of GCNs in expectation. Our theoretical analysis contributes to a deeper understanding of how adversarial perturbations and graph architectures influence generalization performance, which provides meaningful insights for designing robust models. Experimental results on benchmark datasets confirm the validity of our theoretical findings, highlighting their practical significance.
Liyuan Liu, Hong Chen, Weifu Li, Tieliang Gong, Hao Deng, Yulong Wang. Trajectory-Dependent Generalization Bounds for Pairwise Learning with φ-mixing Samples, IJCAI 2025.
最近的研究表明随机梯度下降算法所形成的迭代参数是满足一些条件的随机微分方程。因此分形维数被用来研究独立同分布条件下(i.i.d.)逐点学习模型的泛化能力。而本文不仅将分形维数在泛化分析中的应用推广到了成对学习中,还为varphi-mixing样本下的成对学习建立泛化误差界。由于去掉了i.i.d.的假设,以前的分析技术不适用于varphi-mixing样本下的成对学习。为了克服这一困难,我们将Clemencon等人[1] 的引理A.1扩展到varphi-mixing的情形下,并使用了借助block技术得到的mc不等式。此外,我们还通过设置恰当的半度量来去除了一般分析框架中所需要的利普希茨连续性。[1] Stephan Clemencon, Gabor Lugosi, and Nicolas Vayatis. Ranking and empirical minimization of u-statistics. The Annals of Statistics, pages 844–874, 2008.
